Drill operation
 Audio for slide 1 (mp3 |6|KB)
Audio for slide 1 (mp3 |6|KB)
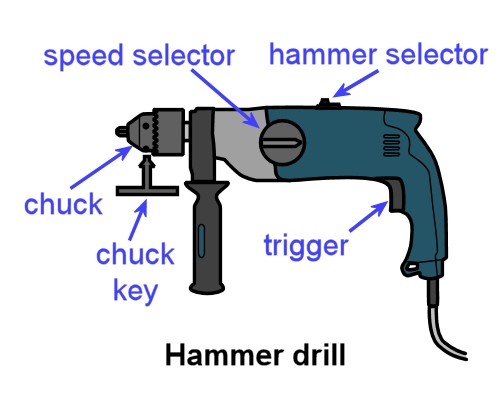
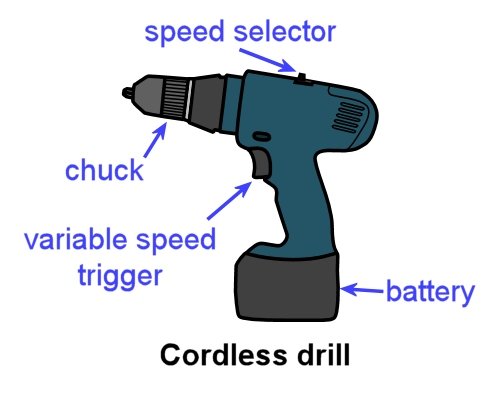
Hand-held drills range from small cordless versions to large hammer drills. As a floor layer, there will be times when you'll need both.
A variable-speed cordless drill is best for driving Phillips head screws and drilling small holes in timber and other non-masonry materials.
However, if you're drilling holes in concrete or brick, you'll need to use a hammer drill with a masonry drill bit.
 Audio for slide 3 (mp3 |6|KB)
Audio for slide 3 (mp3 |6|KB)
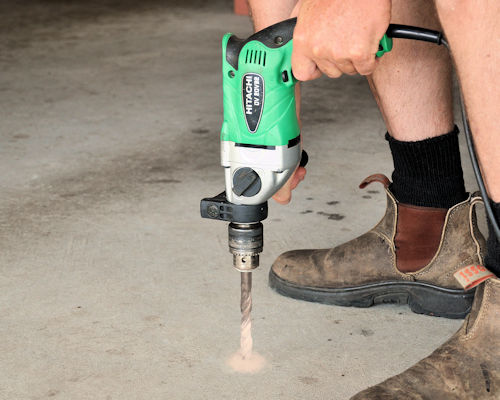
Basic operating procedure
- Secure the material that needs to be drilled if it's loose or not on a stable surface. Insert the drill bit into the chuck and tighten it. If you're using a chuck key, make sure you take the key out before starting the drill.
- Push the drill bit into the surface of the material. If the material is metal, it's best to centre-punch a small indentation into the surface first, so that the tip of the drill bit doesn't skid off the mark when it starts to turn.
- Start up the drill and push down firmly. In general, use slower speeds for hard materials.
- While you're drilling, pull the drill back periodically to clear the waste material from the hole and drill bit. This will help to stop the drill bit from jamming or overheating.
- On larger drills use both hands to hold the drill, with one hand on the side handle, to avoid the problem of the drill suddenly flicking back in the opposite direction if the bit gets jammed.
- On deep holes, pay constant attention to the angle you're holding the drill at, so you don't start to change the direction of the hole while you're drilling. Keep the drill bit turning until you withdraw it from the hole.


Learning activity
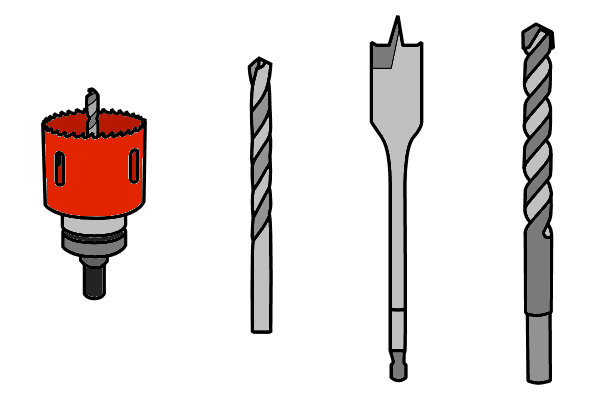
Audio 4 (mp3 |6|KB)The drawings below show four different types of drill bits - spade bit, twist drill, masonry bit and hole saw.
In your workbook, write the correct name for each drill bit under its corresponding drawing.
Then indicate which types of materials it is suitable for drilling into by ticking the correct box or boxes.
Your choices will be wood-based, fibre cement, metal and concrete.